Bonsai trees have been a part of Eastern cultures for centuries, and their symbolism has evolved over time. In Eastern cultures, bonsai trees are considered a form of art that represents harmony and balance. The art of bonsai originated in China over a thousand years ago and was later introduced to Japan, where it became an integral part of Japanese culture.
Bonsai trees are not just miniature trees; they are a form of art that requires skill and patience. In Eastern cultures, bonsai trees are seen as a symbol of patience, discipline, and perseverance. The art of bonsai requires the artist to prune and shape the tree over time, representing the idea of shaping one’s life through discipline and perseverance.
In Japan, bonsai trees are often used in meditation practices because they represent the beauty of nature and the importance of finding balance in life. The symbolism of bonsai trees in Eastern cultures is rooted in the idea of creating harmony between man and nature. Through the art of bonsai, people are reminded to appreciate nature’s beauty and strive for balance in all aspects of life.
Historical Significance of Bonsai
Bonsai is a form of art that originated in China and Japan. The term ‘bonsai’ is derived from the Japanese word ‘bon,’ which means tray or shallow container, and ‘sai,’ which means plant or trees. Bonsai trees are miniature versions of full-grown trees and are grown in containers.
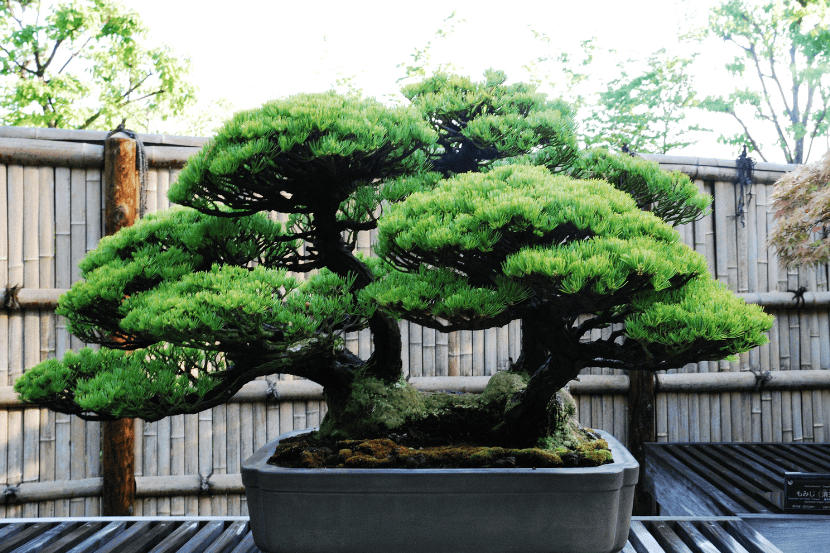

Origins in China and Japan
The origins of bonsai can be traced back to ancient China, where it was known as ‘pun-sai’. The Chinese used this technique to grow miniature trees in pots for ornamental purposes. The art of pun-sai was later introduced to Japan, where it evolved into the art of bonsai.
In Japan, bonsai was developed as a form of art during the Kamakura period (1185-1333). During this time, the Japanese began to cultivate bonsai trees as a form of art and as a way to express their creativity. The art of bonsai continued to evolve during the Edo period (1603-1868), when it became more refined and sophisticated.
Cultural Evolution and Spread
Bonsai trees were initially created for the elite and considered a status and wealth symbol. However, over time, the art of bonsai spread throughout Japan and became more accessible to the general public. Bonsai trees began to be used as a form of meditation and as a way to connect with nature.
The art of bonsai continued to evolve and spread throughout the world. In China, the art of bonsai is known as ‘penjing’ and is considered an integral part of Chinese culture. Penjing is similar to bonsai but includes miniature landscapes and figurines.
Today, bonsai trees are grown and appreciated all over the world. The art of bonsai has become a symbol of patience, dedication, and creativity. It is a form of art that requires skill, knowledge, and a deep appreciation for nature.
Bonsai as an Art Form
Bonsai is a Japanese art form that involves growing miniature trees in pots or containers. The art of bonsai has been around for centuries and has been practiced by many cultures around the world. Bonsai trees are known for their beauty and the intricate pruning techniques used to shape them into miniature masterpieces.
Aesthetic Principles
The aesthetic principles of bonsai are deeply rooted in Japanese culture and Zen Buddhism. The art of bonsai is all about creating a miniature representation of nature that embodies the principles of harmony, balance, and simplicity. The goal is to create a tree that looks like it has been growing in nature for hundreds of years but in a miniature form.
The beauty of bonsai lies in the details. Every aspect of the tree is carefully considered, from the shape and size of the leaves to the placement of the branches. The trunk of the tree is often twisted and gnarled, giving it the appearance of age and wisdom. The pot or container the tree is grown in is also an important aspect of the overall aesthetic. The pot should complement the tree and not detract from its beauty.
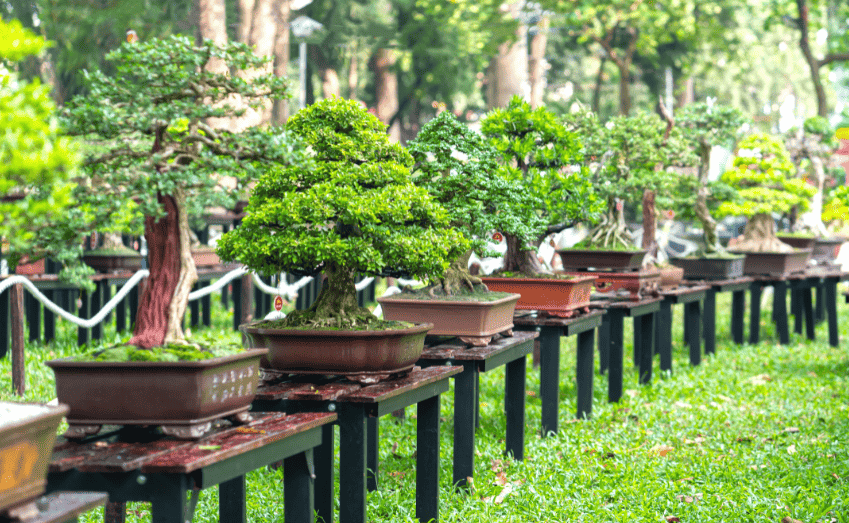

Techniques and Styles
The techniques used to create bonsai trees are complex and require much skill and patience. The trees are pruned and wired to shape them into the desired form. The goal is to create a natural and balanced tree with branches that are evenly spaced and positioned.
There are many different styles of bonsai, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the most popular styles include the formal upright style, the informal upright style, and the cascade style. Each style has its own set of rules and guidelines that must be followed to create a tree that is aesthetically pleasing.

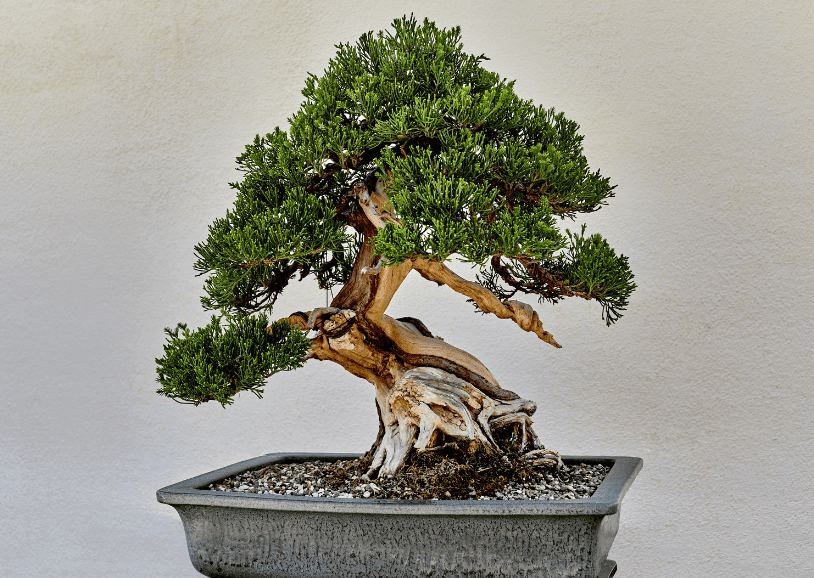

In conclusion, bonsai is an art form that has been practiced for centuries and is deeply rooted in Japanese culture and Zen Buddhism. The aesthetic principles of bonsai are all about creating a miniature representation of nature that embodies the principles of harmony, balance, and simplicity. The beauty of bonsai lies in the details, and every aspect of the tree is carefully considered to create a miniature masterpiece.
Symbolic Meanings in Bonsai
Bonsai trees, deeply embedded in the cultural tapestry of Eastern societies for centuries, transcend their status as mere miniature trees. They profoundly symbolize the intricate relationship between humanity and the natural world. In Eastern cultures, bonsai trees are potent balance, harmony, and strength emblems. Beyond their aesthetic appeal, these meticulously cultivated trees are revered for their spiritual significance, believed to radiate positive energy that fosters peace, health, and unity in their surroundings.
The symbolism of bonsai extends far beyond their physical form. Each carefully pruned branch and sculpted silhouette tells a story of the delicate equilibrium sought between human intervention and the inherent vitality of nature. In the context of Eastern cultures, the art of cultivating bonsai is a reflective practice, inviting individuals to harmonize with the rhythms of the natural world.
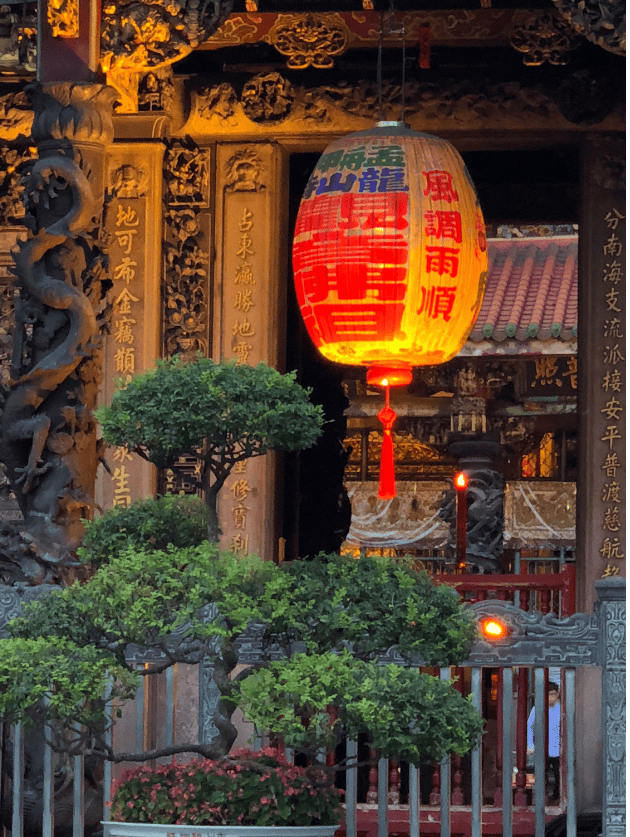

The belief in the spiritual power of bonsai is deeply rooted in the cultural ethos. It is thought that these miniature marvels possess the capacity to infuse their surroundings with a sense of tranquility, promoting physical well-being and unity within communities. The act of tending to a bonsai is, therefore, seen as a way to connect with the spiritual essence of nature and, by extension, to nourish the spiritual well-being of those who engage with these living artworks.
In essence, bonsai trees in Eastern cultures transcend their role as ornamental decorations. They embody a philosophy that celebrates the delicate interplay between humans and the natural world, symbolizing balance, harmony, and strength. The spiritual significance attributed to bonsai underscores their role as agents of positive energy, fostering an environment where peace, health, and unity flourish in harmony with the artful expressions of nature.
Life and Nature
Bonsai trees are a representation of the beauty and simplicity of life. They are a reminder that life is a journey that requires patience and wisdom. The process of growing a bonsai tree requires dedication and care. It is a process that takes time and effort, but the result is a beautiful tree representing life’s essence.
Philosophical and Spiritual Concepts
Bonsai trees are believed to possess a spiritual significance that can bring peace, health, and unity to the environment. They represent the philosophical concept of “less is more” and the idea of finding beauty in simplicity. Bonsai trees are also a symbol of the Japanese Zen philosophy, which emphasizes the importance of living in the present moment and finding inner peace.
In Eastern cultures, the art of bonsai is considered to be a form of meditation. It requires focus and concentration, which can help to clear the mind and promote inner peace. Bonsai trees are also believed to possess healing properties that can promote physical and emotional health.

In conclusion, bonsai trees are more than just miniature trees; they are a representation of the relationship between man and nature. They possess symbolic meanings that can bring balance, harmony, and strength to the environment. The art of bonsai is a reminder that life is a journey that requires patience, wisdom, and dedication.
Bonsai Trees in Practice
Selection and Care
Selecting the right bonsai tree is an important process that requires attention to detail. It is important to choose a species that is appropriate for the climate and environment in which it will be grown. Some common species of bonsai trees include Ficus Bonsai, Jade Bonsai, Chinese Elm, and Juniper Bonsai. Each species has its own unique requirements for care and attention.
Once a species has been chosen, it is important to provide the proper care and attention to ensure its health and longevity. Bonsai trees require regular watering, fertilization, and pruning. The soil must be well-drained, and the tree must be placed in an area with adequate sunlight and ventilation.
Common Species and Varieties
Ficus Bonsai is a popular species of bonsai tree that is easy to care for and can be grown indoors or outdoors. It requires moderate watering and can be grown in a variety of soil types.
Jade Bonsai is another popular species that is known for its thick, fleshy leaves and attractive appearance. It requires infrequent watering and can be grown in a variety of soil types.
Chinese Elm is a hardy species that is known for its resistance to disease and pests. It requires moderate watering and can be grown in a variety of soil types.
Juniper Bonsai is a species that is known for its attractive foliage and unique appearance. It requires infrequent watering and can be grown in a variety of soil types.
Overall, selecting and caring for a bonsai tree requires attention to detail and a commitment to providing the proper care and attention. With the right species and care, a bonsai tree can provide years of enjoyment and beauty.
Cultural and Personal Significance
Bonsai trees hold a deep cultural and personal significance in Eastern cultures, particularly in Japan. They are viewed as a symbol of love, joy, and value for living things. Bonsai trees are also considered an art form, with the practice of cultivating and shaping them dating back centuries.
Bonsai in Everyday Life
In Japanese culture, bonsai trees are often displayed in homes and workplaces as a way to bring serenity and tranquility to the environment. They are believed to have a calming effect on the mind and body and can help reduce stress and anxiety. Bonsai trees are also seen as a way to nurture and care for living things, which is an important value in Eastern cultures.

Gift-Giving and Collecting
Bonsai trees are often given as gifts in Eastern cultures, especially in Japan. They are considered a thoughtful and meaningful present, symbolizing good fortune, wealth, and passion. Bonsai trees can also be collected as a hobby, with enthusiasts valuing the beauty and uniqueness of each tree.
In addition to their cultural significance, bonsai trees are also believed to have spiritual significance in Eastern cultures. They are often associated with feng shui, a practice that aims to create a harmonious and balanced environment. Bonsai trees are believed to bring good luck and fortune to those who display them in their homes or workplaces.
Bonsai trees hold a special place in Eastern cultures, representing knowledge, serenity, and the nurturing of living things. They are a symbol of the beauty and complexity of nature, and a reminder to appreciate the small things in life.
Modern Bonsai and Global Influence
Bonsai has come a long way from its ancient roots in China and Japan. Today, bonsai is a global phenomenon, with practitioners and enthusiasts all over the world. The art of bonsai has undergone significant changes and adaptations over the years, reflecting its practitioners’ changing times and tastes.
Adaptation and Innovation
In recent years, bonsai has seen a surge in popularity, particularly in Western cultures. This demand has led to the creation of new styles and techniques, as well as the integration of modern technologies. For example, some bonsai practitioners now use 3D printing technology to create custom pots and other bonsai accessories. Additionally, some bonsai artists are experimenting with new materials, such as wire mesh, to create more intricate and complex bonsai designs.
Bonsai in the Western World
The spread of bonsai to the Western world has also had a significant impact on the art form. Western bonsai practitioners have brought their own unique perspectives and techniques to the art form, shaping it in new and exciting ways. For example, some Western bonsai artists focus on creating naturalistic, landscape-inspired designs, while others focus on creating more abstract, sculptural designs.
Overall, the global influence on bonsai has brought new energy and innovation to the art form while still maintaining its traditional roots. As bonsai continues to evolve and adapt, it remains a beloved and respected art form around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the cultural significance of bonsai trees in Eastern traditions?
Bonsai trees have been an important part of Eastern cultures, particularly in China and Japan, for centuries. They are seen as symbols of harmony, balance, and a connection to nature. In Eastern traditions, bonsai trees are also believed to bring good luck and fortune to their owners.
How do bonsai trees represent spirituality in Eastern philosophies?
Bonsai trees are often associated with Zen Buddhism, which emphasizes the importance of mindfulness and meditation. In Eastern philosophies, bonsai trees are seen as a way to connect with the natural world and achieve inner peace and tranquility.
What role does the bonsai tree play in the practice of Feng Shui?
In Feng Shui, the ancient Chinese practice of arranging objects to promote harmony and balance, bonsai trees are believed to bring good luck and positive energy to a space. They are often placed in the wealth or prosperity corner of a room to attract abundance and success.
Can you explain the historical origins of bonsai cultivation in Eastern cultures?
The cultivation of bonsai trees can be traced back to ancient China, where miniature trees were grown in pots as early as the Han dynasty (206 BCE-220 CE). The practice then spread to Japan, where it became an art form and a symbol of refinement and elegance.
What meanings are associated with different species of bonsai, like juniper or ficus, in Eastern cultures?
Different species of bonsai trees are associated with different meanings in Eastern cultures. For example, the juniper bonsai is often seen as a symbol of longevity and strength, while the ficus bonsai is associated with prosperity and good fortune.
How is the art of bonsai linked to Buddhist principles and practices?
The art of bonsai is closely linked to Buddhist principles and practices, particularly the idea of wabi-sabi, which emphasizes the beauty of imperfection and impermanence. Bonsai trees are also seen as a way to cultivate mindfulness and connect with the natural world, which are important tenets of Buddhism.



2 thoughts on “Tiny Giants: Unveiling Bonsai’s Deep Cultural Symbolism”
Comments are closed.