Creating a drought-resistant garden is an efficient and aesthetically pleasing way to cultivate plants even in arid conditions. Potted succulents are especially suited for this purpose due to their low water requirements and diverse variety.
These hardy plants thrive in dry environments, making them the perfect candidates for gardens that need to conserve water while still delivering visual interest and a touch of greenery to outdoor spaces.

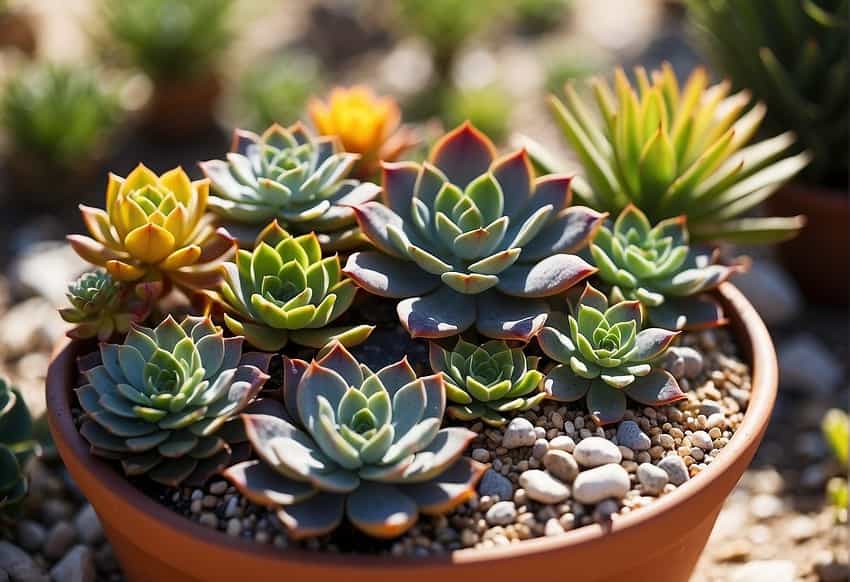
Selecting succulents thoughtfully and pairing them with suitable containers empowers gardeners to craft a portable, resilient collection resistant to both heat and drought.
Embracing a succulent container garden provides the canvas for flexible arrangements, fostering personal expression and unleashing creativity in design.
With meticulous planning, these gardens become textured tapestries, adorned with a spectrum of colors and forms, effortlessly bestowing a touch of sophistication upon patios, balconies, and terraces.
Integrating drought-tolerant succulents into garden practices not only conserves water but also guarantees the sustainable longevity of the garden.
Incorporating locally sourced, climate-appropriate plants further fortifies the garden’s resilience, diminishing the need for constant attention and amplifying the sheer delight of gardening. This approach ensures more time for savoring the beauty of a potted succulent arrangement that effortlessly thrives in arid conditions.
Understanding Drought and Its Impact on Gardening
Drought is characterized by an extended period of insufficient rainfall, leading to water scarcity that profoundly affects ecosystems, economies, and daily life. In gardening, a lack of water can hinder plant growth, reduce yield, and increase susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Gardeners must recognize the signs of drought stress in plants, which often include:
- Wilted leaves: A plant’s inability to retain water leads to a loss of turgor pressure, causing leaves to droop.
- Dry soil: The soil appears crumbly, and water does not infiltrate well.
- Leaf scorch: Margins of leaves turn brown or yellow as the plant’s ability to photosynthesize is impacted.
When designing drought-resistant gardens, the choice of plants is crucial. Succulents are ideal as they store water in their leaves, stems, or roots.
Additionally, gardeners might consider implementing wildlife-friendly practices that support local biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
A strategic approach includes:
- Mulching: Applying a protective layer of mulch helps retain moisture, moderates soil temperature, and limits weed growth.
- Soil Improvement: Incorporating organic matter improves water retention and supports plant health.
- Water Conservation: Techniques such as drip irrigation and watering at cooler times of the day minimize evaporation losses.
Succulents 101: Characteristics and Benefits
Succulents are renowned for their water-storing capabilities and drought-resilient nature, providing an array of textures and forms suitable for diverse garden designs.
Defining Succulents and Their Drought-Resistant Nature
Succulents are plants with water-storing tissue in their leaves, stems, or roots, enabling them to thrive in arid conditions. This unique adaptation allows them to maintain moisture and endure prolonged dry periods, making them highly drought-tolerant.
The ease of care for these drought-resistant plants stems from their efficient use of water, which is a significant advantage in landscapes where water conservation is a priority.
The Variety of Succulent Plants
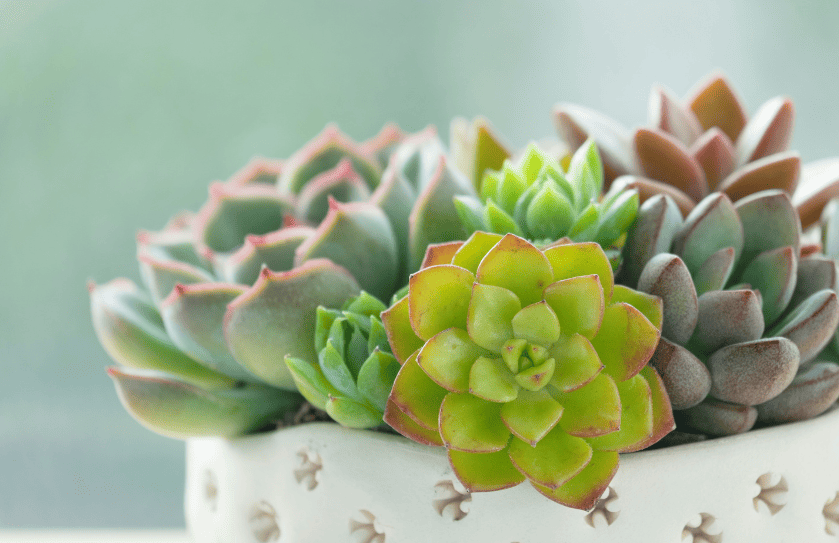
With their varied shapes and sizes, succulents offer a wide range of textures, from the soft and fleshy leaves of Echeveria to the rigid and spiky appearance of the Aloe species.
There is a spectrum of drought-resistant options available, each with its own specific care requirements and aesthetic appeal. Here are some examples:
- Sempervivum (Hens-and-Chicks): Offers rosettes that multiply readily.
- Echeveria: Known for its attractive, symmetrical rosettes and a variety of colors.
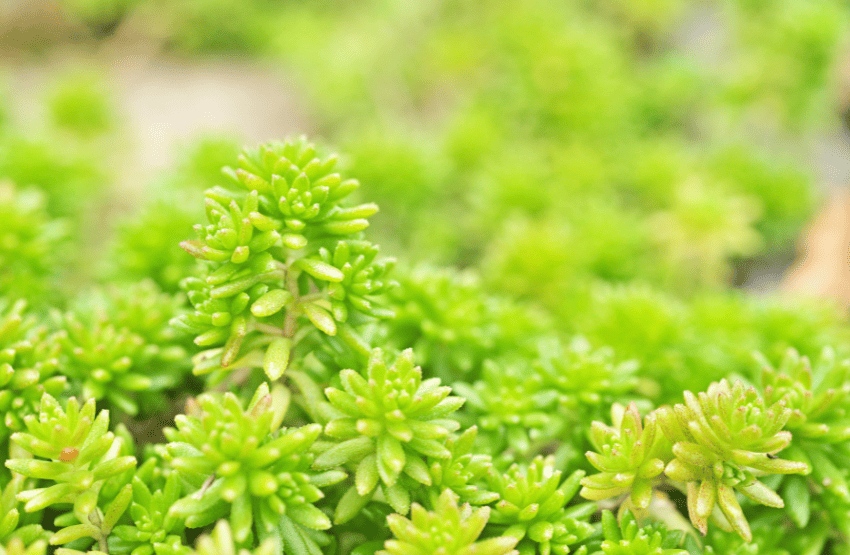
- Sedum: Displays a carpet-like growth, ideal for ground cover.
Incorporating these diverse plants into garden spaces not only adds visual interest but also ensures a resilient landscape capable of withstanding dry climates.
Designing Your Succulent Garden

Crafting a drought-resistant garden calls for careful selection of plants and a strategic design to create aesthetic appeal. Focusing on succulent container gardens enables one to exercise creativity in a small space while ensuring the garden is both functional and enduring.
Selecting the Right Succulents
When choosing succulents, it’s imperative to opt for those that are drought-tolerant and well-suited to your local climate.
Plants like agave and echeveria are renowned for their resilience and ability to thrive with minimal water. For a layered look, consider incorporating sedum species, which offer a range of textures and colors.
| Drought-Tolerant Succulents | Light Requirements | Water Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Agave | Full sun | Low |
| Echeveria | Full sun to partial shade | Low |
| Sedum | Full sun to partial shade | Low |


Creating a Cohesive Garden Plan
A well-planned succulent container garden should have a balance of heights, colors, and textures.
Start with taller species like agave as focal points, then add clusters of rosette-forming echeveria, and finish with trailing sedum to soften edges and add fullness. Space plants, according to their size at maturity to prevent overcrowding.
- Tall Plants: Agave
- Mid-Height Plants: Echeveria
- Groundcover/Trailing Plants: Sedum
Incorporating Decorative Elements
Besides plants, incorporating decorative elements can elevate the visual interest of your drought-tolerant garden.
Use pebbles or river rocks to create a clean look and improve drainage around the succulents. For a striking contrast, place ornamental items or art among the plants, choosing materials and themes that complement the garden’s palette and structure.
Best Practices for Potted Succulent Gardens
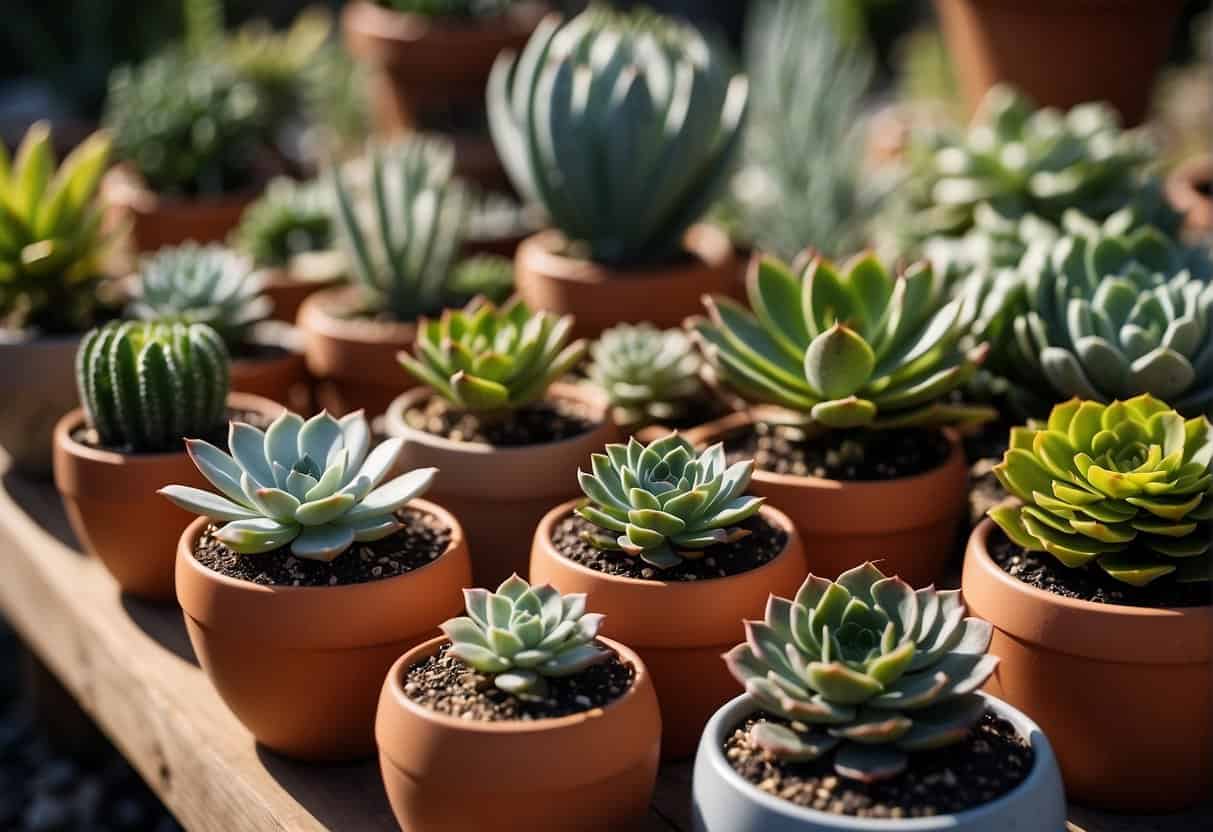

Creating a thriving potted succulent garden requires careful selection of containers, attention to soil and drainage, and an understanding of the plant’s sunlight and temperature needs.
Choosing Containers and Pots
When selecting containers for succulent gardens, prioritize those with sufficient drainage holes to prevent water from pooling at the base.
The material of the pot should allow for heat dissipation and adequate airflow, with terra cotta being a popular choice due to its porous nature.
Pots should be proportionate to the size of the succulent to ensure balance and stability while allowing room for growth.
Soil and Drainage Requirements
A well-draining potting mix is critical for succulent health.
Mixes specifically designed for cacti and succulents typically include components like perlite, pumice, or coarse sand to facilitate proper drainage and prevent root rot.
It is essential to avoid mixes with water-retaining crystals, as succulents prefer a drier environment.
The Role of Sunlight and Temperature
Succulents generally thrive in full sun to partial shade, requiring around six hours of sunlight a day.
They are best positioned in areas where they can receive morning sunlight and partial afternoon shade, as intense heat can scorch the leaves.
Temperature control is paramount; succulents prefer a climate that mimics their natural desert habitat, which usually ranges from 70°F to 80°F (21°C to 27°C) during the day and cooler at night.
Plant Care and Maintenance

Creating a thriving drought-resistant garden with potted succulents requires specific care techniques to cope with low water availability while maintaining plant health.
Proper watering and fertilization are the cornerstones of plant care for these resilient species.
Watering Techniques and Conservation
Succulents store water in their leaves and stems, which makes them excellent at surviving dry conditions.
To maximize water efficiency, gardeners should employ a “soak and dry” method, fully saturating the soil and then allowing it to dry out completely before the next watering.
This mimics natural drought conditions, encouraging deep-root growth and resilience.
Collecting rainfall in barrels to water plants is another effective conservation strategy, reducing water usage from the tap.
One should always monitor the soil’s moisture level using a simple finger test or a soil moisture meter to prevent over-watering, which can lead to root rot.
- Frequency: Water deeply when the soil is dry. During peak summer, this may be once a week; in cooler months, less often.
- Methods: Use drip irrigation or watering cans to target the water directly to the roots, avoiding waste.
Fertilizing and Nourishing Your Plants
Even low-maintenance succulents benefit from occasional feeding. They need less fertilizer than other plants since they are adapted to environments with few nutrients.
A balanced, water-soluble fertilizer can be applied to provide essential nutrients without overwhelming the plants. It’s best utilized during the active growing season – spring and summer – and limited during the dormant period in fall and winter.
- Organic Matter: Adding small amounts of organic matter can improve soil texture and nourishment.
- Fertilizer Choice: Seek out fertilizers formulated for cacti and succulents for optimal plant health.
Selecting and Pairing Companion Plants

When creating a potted succulent garden that is resistant to drought, the selection of companion plants is crucial. Companion plants should have similar water requirements and create a cohesive look. They also contribute to the succulents’ health by providing shade, improving soil quality, or attracting beneficial insects.
Ideal Companion Plants:
- Stonecrop (Sedum): Thrives in dry conditions and comes in a variety of colors and sizes.
- Yucca: Offers architectural height and is extremely drought-tolerant.
Considerations for Pairing:
- Size & Structure: Taller plants like yucca should be placed towards the back of the arrangement, with ground-hugging stonecrop varieties at the forefront.
- Color Harmony: Select companion plants with colors that complement or contrast with the succulents for visual interest.
| Succulents | Companion Plants | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Small Rosettes | Stonecrop | Fills space evenly |
| Large, Spiky | Yucca | Adds height |
Complementary Elements:
- Rocks & Stone: Add these elements to reflect a natural, arid environment and aid in drainage.
- Compost: Incorporate a small amount of compost to enrich the potting mix, which succulents and companions like yucca appreciate.
Succulent Species Showcase

Succulent plants are renowned for their resilience and come in an astonishing range of forms. This showcase spotlights both popular and unique succulents, all well-suited to survive in a parched environment.
Popular Succulent Varieties
Agave: Known for its striking rosettes, this genus boasts active members like the compact ‘Victoriae-Reginae’, which stands out for its jade and cream variegated pattern.
Sedum: Often used as groundcover, Sedum varieties like the ‘Pale Sedum’ provide a striking contrast with their light green hues and are known for spreading shoots.
Jade Plant (Crassula ovata): A beloved houseplant, this drought-tolerant succulent is characterized by its thick, shiny leaves and woody stems.
Dudleya: Native to California, Dudleyas are a testament to the diversity of succulents, with their rosette shape and powdery coating that combats drought.
- Flowering Succulents: Many succulents, like various types of Echeveria, produce vibrant flowers, adding a splash of color to the drought-resistant garden.
Showcasing Diverse Beauties
Variety of Textures: Succulents offer a range of textures, from the rubbery and fleshy leaves of jade plants to the soft, plushy feel of some Sedum species.
Cholla (Cylindropuntia): The cholla cactus features cylindrical stems covered with sharp spines, creating a unique visual and textural impact.
Carpobrotus edulis: Also known as the highway ice plant, this succulent forms a dense mat and stands out with its daisy-like flowers and succulent triangular leaves.
- Types of Succulents: The variety found within the world of succulents is vast, with over 10,000 varieties, each suited to different ecological niches and aesthetic preferences.
Year-Round Care and Seasonal Concerns

Creating a drought-resistant garden with potted succulents requires an understanding of the climate’s seasonal changes and how to mitigate extreme weather events to ensure plant health throughout the year.
Adapting to Climate Variations
In arid regions, succulents thrive due to their natural design to conserve water. However, gardeners must account for temperature fluctuations that can impact plant growth.
During the hotter months, it is crucial to provide partial shade to prevent sunburn. Conversely, in cooler temperatures, one must move potted succulents to sunny spots or even indoors to maintain the warmth they need for optimal health.
- Summer: Position pots in locations where they will receive morning sunlight and afternoon shade.
- Winter: Increase light exposure; if necessary, use grow lights to simulate natural sunlight.
Handling Extreme Weather Conditions
Apart from regular climatic patterns, gardeners must be prepared for extreme weather events such as heatwaves, cold snaps, and harsh winds. Potted succulents can be particularly vulnerable as their root systems are confined to containers.
- Heatwaves: Utilize shading cloths and increase watering frequency without overwatering.
- Cold Snaps: Bring pots inside or wrap them with frost blankets to insulate against the cold.
- Strong Winds: Place pots in sheltered areas, or use heavier containers to prevent toppling.
Enhancing Sustainability Through Xeriscaping

Xeriscaping is a landscaping philosophy that conserves water by utilizing drought-resistant plants and efficient watering practices. This approach is particularly valuable in creating sustainable garden spaces where water resources are scarce or conservation is a priority.
Sustainability in gardening is achieved through careful selection of plants and water-wise techniques, ensuring that gardens thrive with minimal environmental impact.
- Plant Selection: Choose low-growing and native plants that are well-adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. Such plants typically require less water and care than non-native species.
- Water Usage: Implement drip irrigation or soaker hoses that deliver water directly to the roots, where it’s most needed, thus reducing water usage.
Incorporating xeriscaping into a potted succulent garden enhances sustainability by:
- Reducing Water: Potted succulents require infrequent watering compared to traditional garden plants. Their ability to store water in leaves or stems allows for longer intervals between watering, conserving valuable resources.
- Maintenance: Succulents are generally low-maintenance, which not only saves water but also reduces the need for fertilizers and pesticides, further contributing to an eco-friendly garden.
- Soil Composition: Using the correct soil mix, which often includes sand and pebbles, ensures good drainage and mimics the natural habitats of these drought-resistant plants, promoting sustainability through an understanding of plant needs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

When tending to a potted succulent garden, you may encounter several common issues related to drainage, water, and sunlight exposure. Here’s how to identify and address them confidently and clearly.
Overwatering: Succulents require less water than other plants. Signs of overwatering include mushy, yellowing leaves. To remedy this, adjust watering techniques. Allow the soil to dry out completely between waterings and avoid water-retentive potting mixes.
| Symptom | Possible Issue | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Mushy leaves | Overwatering | Let soil dry; water less |
| Wilted leaves | Underwatering | Water thoroughly |
| Burnt leaves | Excessive sunlight | Provide shade |
| Pale leaves | Inadequate sunlight | Increase light exposure |
Drainage: Good drainage is crucial—succulents dislike standing water. Ensure pots have drainage holes and use a well-drained potting mix. If a pot lacks holes, consider drilling some or using a different pot that allows excess water to escape freely.
Sunlight: Succulents thrive in ample sunlight, but too much direct exposure can lead to scorched leaves. Conversely, inadequate light can cause succulents to stretch out and lose color. Strike a balance by monitoring the plant’s response to its light source and adjust as necessary. Some succulents may prefer filtered light, especially in hotter climates.
Creative Ideas for Displaying Potted Succulents

When designing a drought-resistant garden, the use of succulents in various containers can create an aesthetically pleasing and water-efficient display. Here are some creative ideas to help gardeners showcase their potted succulents:
- Tiered Arrangements: Utilize stands with multiple levels to create a dynamic display that gives each succulent its moment in the sun. By arranging pots in ascending order, even the smallest succulent can become a focal point.
- Mixed Textures: Combine succulents with different leaf textures in a single pot for a visually engaging display. Soft, spiky, and rubbery leaves side by side can highlight the unique beauty of each plant.
- Hanging Pots: Suspend succulent containers from the patio or porch to add a floating, lush green element to the area. Hanging baskets can also save valuable ground space for other garden essentials.
- Decorative Pots: Choose pots that complement the succulents’ form and color. Brightly colored or patterned containers can add a pop of color, while more neutral or earthy tones can let the plants stand out.
- Grouping by Color or Size: Cluster succulents by color shades or sizes to create a cohesive theme. Grouping them can contribute to a more structured look, whether it’s a gradient of greens or a crescendo from small to large sizes.
- Reclaimed Objects as Pots: Integrate an eco-friendly element by using reclaimed items like old boots, teacups, or wine barrels as succulent pots. This not only recycles but also lends a unique and personal touch to the garden.
Expanding Beyond Succulents

While succulents are a staple in drought-resistant gardening, incorporating a variety of other plants such as perennials, shrubs, and trees can create a richer, more diverse garden ecosystem. Annuals and less common varieties also offer unique textures and colors, complementing your succulent collection.
Incorporating Perennials, Shrubs, and Trees
Perennials: They are the backbone of a resilient garden, requiring minimal maintenance once established. Plants like lavender and Russian sage not only withstand dry conditions but also add a fragrant dimension to the garden space.
- Drought-Tolerant Perennials:
- Yarrow (Achillea millefolium)
- Catmint (Nepeta faassenii)
Shrubs: Adding shrubs to the landscape invites different levels and depths, with some varieties like the butterfly bush (Buddleja) attracting wildlife.
- Shrub Examples:
- Butterfly Bush (Buddleja)
- Wormwood (Artemisia)
Trees: Trees not only provide shade but also serve as windbreaks and improve the microclimate of your garden. Drought-resistant trees like mesquite (Prosopis) or palo verde (Cercidium) can be focal points.
- Tree Selection:
- Mesquite (Prosopis)
- Palo Verde (Cercidium)
Exploring Annuals and Less Common Varieties
Annuals: While often overlooked in dry gardens, some annuals are surprisingly resilient and can bring a burst of color that changes with the seasons.
- Annuals for Dry Conditions:
- California Poppy (Eschscholzia californica)
- Globe Amaranth (Gomphrena globosa)
Less Common Varieties: Exploring cultivars with unique drought coping mechanisms can introduce novel features and textures to your garden.
- Unique Cultivars:
- Hens and Chicks (Sempervivum ‘Ruby Hearts’)
- Ice Plant (Delosperma ‘Fire Spinner’)
Garden Accessories and Embellishments
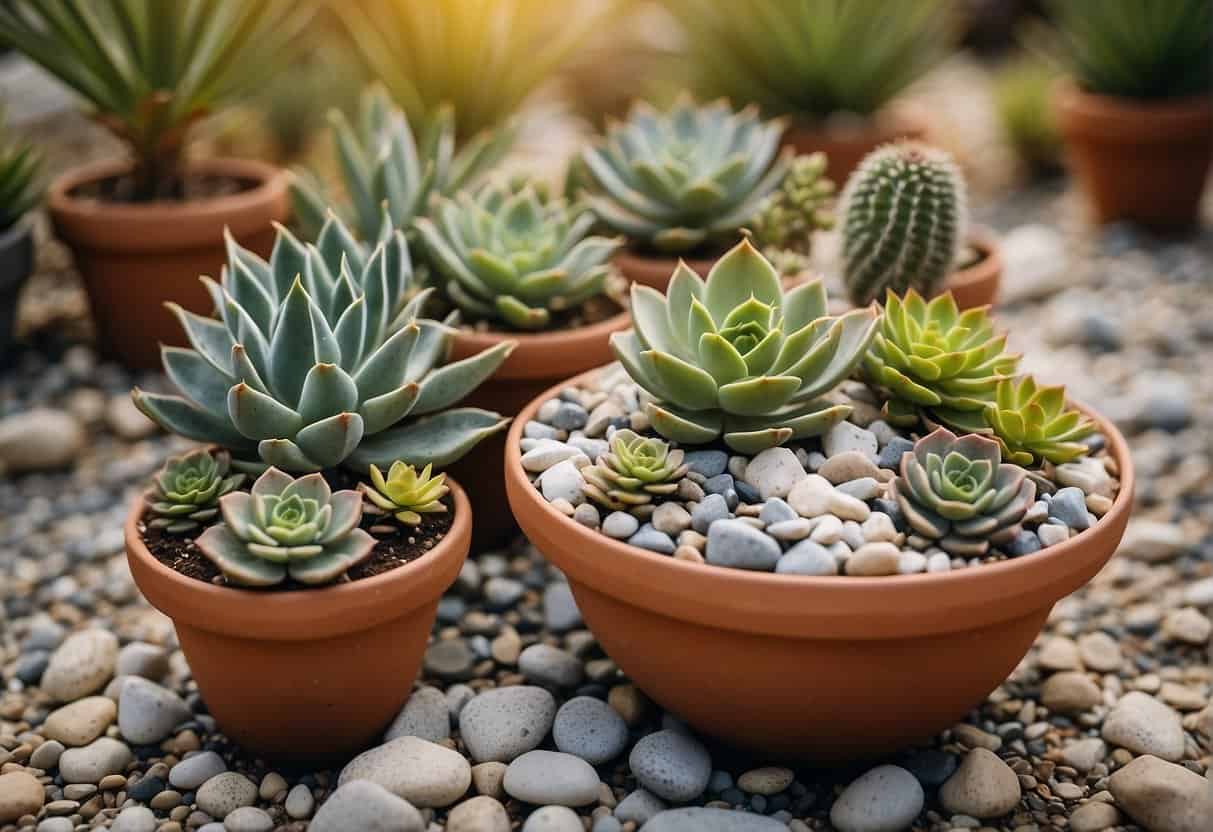

Creating a drought-resistant garden entails more than just selecting the right plants; it involves designing a space that is both functional and visually appealing. Accessorizing your potted succulent garden with the right embellishments can enhance the overall aesthetic and create a serene environment.
Making Use of Stones and Gravel
Incorporating stones and gravel into a potted succulent garden provides a decorative element that complements the plants’ natural beauty. Stonecrop, a type of succulent, thrives when paired with a surrounding of stones that reflect sunlight and reduce water evaporation. Here’s a simple way to employ these materials:
- Crushed Gravel: Spread a layer of crushed gravel around the base of your potted succulents to create consistency and improve drainage, reducing the risk of root rot.
Adding Water Features for Appeal
A water feature can serve as a focal point in a succulent garden. The sound of water from a fountain or miniature pool adds a soothing backdrop and attracts wildlife such as birds and butterflies. Consider these ideas:
- Fountain: Choose a solar-powered fountain to minimize maintenance and resource use while providing the gentle sound of flowing water.
- Pool: A shallow ornamental pool with pebbles and water plants can create a microclimate that benefits your drought-resistant plants.
Practical Tips for Gardening in Drought-Prone Areas
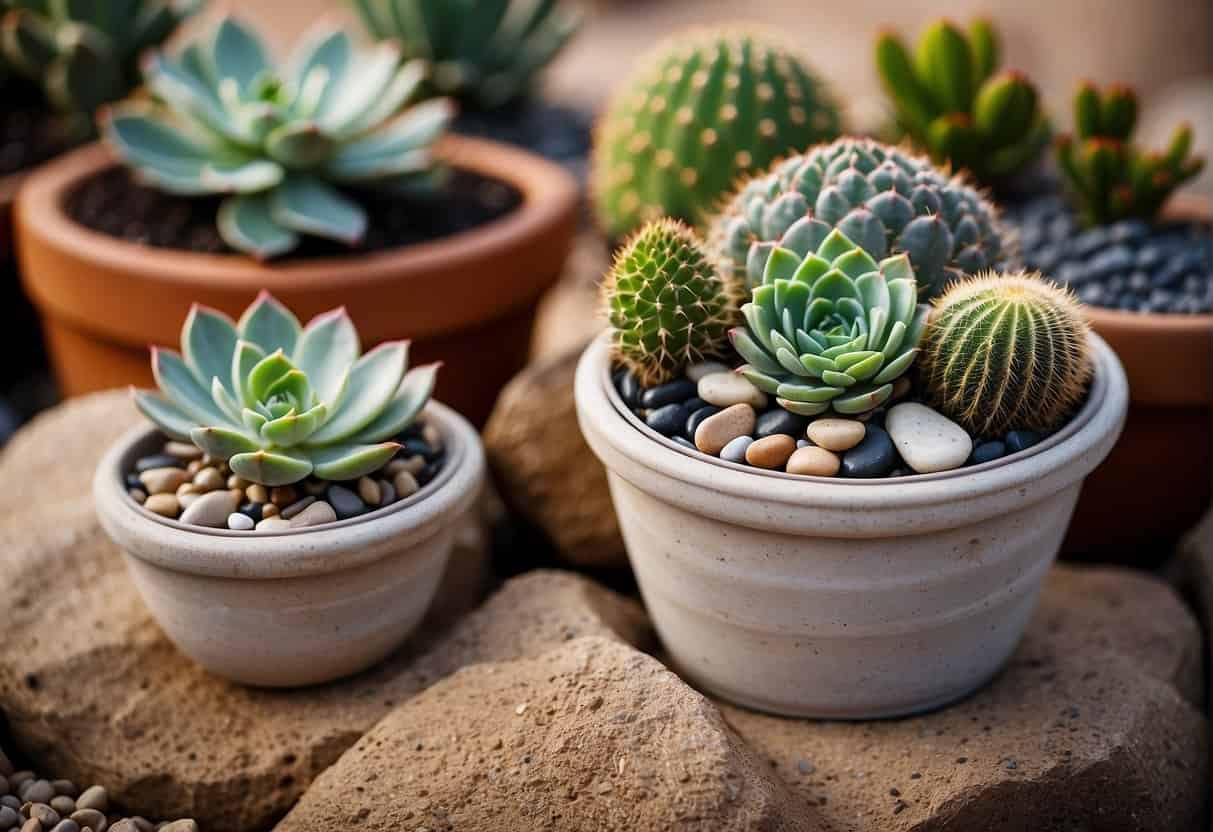

In areas where water scarcity is common, creating a drought-tolerant garden, especially with potted succulents, can be both a practical and aesthetic choice. These gardens not only conserve water but also withstand the challenging weather conditions.
Selection of Plants: Opt for succulents and other plants with water-storing tissue, such as Aloe vera and Agave. These plants have adapted to survive with minimal moisture and are ideal for potted settings.
Irrigation Techniques: Make use of efficient irrigation methods, for instance, drip irrigation. This technique delivers water directly to the roots, thereby reducing evaporation and conserving water.
- Soil Preparation: Amend soil with organic matter to enhance its water retention capabilities without compromising drainage.
- Mulching: Apply a layer of mulch around plants to help retain soil moisture and reduce the need for frequent watering.
- Watering Schedule: Water plants during the cooler parts of the day, like early morning or late evening, to minimize water loss.
- Grouping Plants: Arrange plants with similar water requirements together. This strategy helps in creating “hydrozones” and prevents overwatering of drought-resistant varieties.
Inspiration from Worldwide Drought-Resistant Landscapes
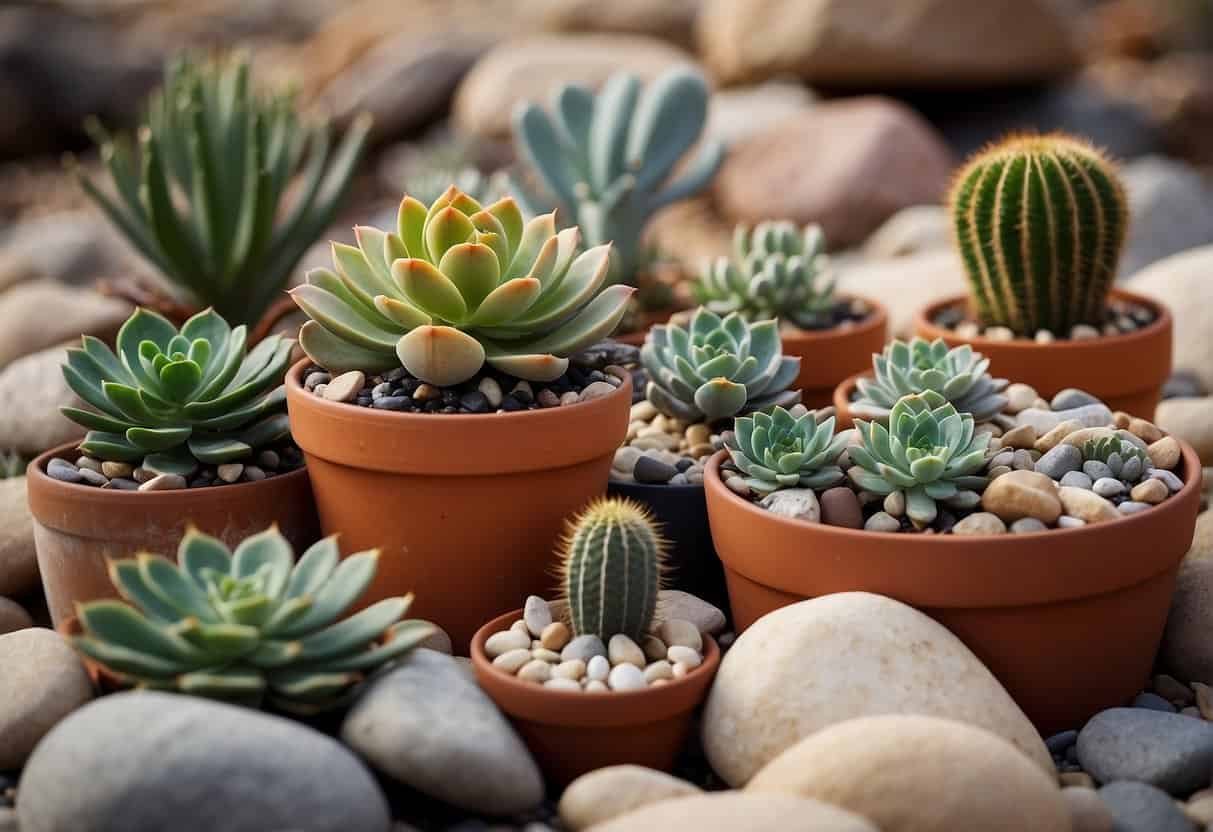

When creating a potted succulent garden designed to withstand dry conditions, one can draw inspiration from various drought-resistant landscapes around the globe. These gardens embrace the principles of xeriscaping, a method that reduces or eliminates the need for supplemental water from irrigation.
In North America, the concept is embodied by the savvy use of native species like the Joshua Tree or the Prickly Pear Cactus. Gardeners often incorporate gravel or stone as mulch to minimize water evaporation and suppress weeds.
| Region | Characteristics | Notable Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Mediterranean | Well-draining soil, gravel mulch | Lavender, Rosemary |
| Californian | Native species, efficient irrigation | California Poppy, Toyon |
| Southwestern | Large rocks, cacti | Agave, Texas Sage |
The Mediterranean basin offers further inspiration with its herbal tapestry. Plants in this area are adapted to prolonged summer dry spells, evolved with silver or gray foliage to reflect sunlight and reduce water loss.
Africa’s arid regions showcase landscapes where every drop of water is used to its fullest effect. Succulents like Aloe Vera thrive here, storing moisture in their thick leaves. Baobabs and Acacia trees are interspersed among xerophyte communities, providing shade and reducing soil temperature.
Australians have developed stellar drought-tolerant gardens, utilizing native flora such as Kangaroo Paw and Woolly Bush, which are not only resilient but also add exceptional beauty to potted arrangements.
Understanding the Environmental Benefits of Drought-Resistant Plants

Drought-resistant plants offer significant environmental advantages, particularly in regions where water scarcity is a growing concern. These plants are typically adapted to low-water environments, making them an ideal choice for sustainable landscaping. By incorporating drought-resistant plants into gardens, one can contribute to conserving water—a critical resource facing increasing demand and limited supply.
Key benefits include:
- Water Conservation: These plants require less frequent watering than their non-drought-resistant counterparts, thereby reducing overall water usage.
- Soil Preservation: They often have deep root systems that help to stabilize soil and prevent erosion, even in arid conditions where water is limited.
- Habitat Support: Drought-resistant plants can provide essential habitats for local wildlife, creating a biodiverse environment even during dry spells.
Eco-Friendly Maintenance: With less need for irrigation, fertilizers, and pesticides, these plants enable a drought-resistant garden to maintain its vitality with minimal environmental impact. They’re often resilient to pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
Energy Savings: The reduced need for watering also translates into energy savings, as less power is required for irrigation systems. In large-scale applications, this effect can be substantial.
Cultivating Community and Sharing Success
Creating a drought-resistant garden, specifically one that showcases potted succulent varieties, can become a cornerstone for community engagement and success sharing. Succulents, with their minimal water needs and variegated forms, are excellent candidates for such gardens.
Community Gardens are often limited in space, making potted succulents a practical choice. Through sharing knowledge on potting mixes and care tailored for these resilient plants, community members can ensure a collectively thriving garden. For example, Birds and Blooms recommends a well-drained potting mix without water-retaining crystals to accommodate the dry-loving nature of succulents.
Workshops and Plant Swaps play a pivotal role. Organizing these events enables the exchange of both succulent cuttings and expertise. It’s a chance for community members to showcase their own flashy flowering succulents and learn about others’ successful techniques.
| Activity | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Plant Swaps | Exchange of cuttings and stories |
| Care Workshops | Education on drought-tolerance |
| Community Potting | Collective garden beautification |
Community Success Stories, such as those from the Lifesavvy guide to making gardens drought-tolerant, inspire further participation and growth. They demonstrate the tangible benefits of a drought-tolerant garden, from water conservation to enhanced local biodiversity.
Incorporating drought-tolerant garden structures can serve the dual purpose of supporting plant life and fostering community interaction. As detailed by Coohom, these can be instrumental in addressing the challenges of poor soil quality and space management.
Concluding Thoughts
When considering the establishment of a drought-resistant garden, potted succulents stand as a testament to both sustainability and aesthetic appeal. They effortlessly marry the demand for low water usage with a striking diversity in form and hue.
Reflecting on the Resilient Beauty of Succulents
Succulents are a remarkable choice for those who wish to cultivate a garden resilient to arid conditions. Drought-resistant plants like these not only thrive with minimal hydration but also serve as a vibrant centerpiece to any setting. Enthusiasts are often compelled by the diverse beauty of succulents, which can range from the deep purples of ‘Purple Mojo’ to the pale greens of Echeveria. Their ease of care makes them an ideal choice for gardeners at any skill level, often only requiring a proper soil mixture that promotes good drainage—a critical factor in preventing root rot.
Succulents should never be an afterthought in garden design. Their ability to store moisture allows them to endure longer periods without water, making them a forefront option for eco-conscious gardeners. Their thick, fleshy leaves vary in shape and size, offering a visual feast for the eyes and creating a dynamic landscape even in the driest climates.
In short, incorporating succulents into a garden space is a decision that reflects both a practical approach to water conservation and a desire to surround oneself with the natural, sculptural forms of these enduring plants.
Resources and Further Reading
To further develop one’s understanding of creating a drought-resistant garden with potted succulents, a selection of authoritative resources is invaluable. Below is a curated list that gardeners can reference:
- Books: Enthusiasts might consider “Succulents Simplified” by Debra Lee Baldwin, a recognized expert. She offers practical tips on design and care for these resilient plants.
- Websites:
- Birds and Blooms provides a guide on creating a succulent container garden, highlighting the importance of using the right potting mixture and avoiding mixes that retain too much moisture.
- Better Homes & Gardens showcases 25 diverse succulent container ideas to inspire designs that are both heat and drought tolerant.
- Online Articles: The San Diego Union-Tribune featured an article with designing tips that emphasized the use of repetition and color contrast to enhance the visual impact of succulent gardens.
- Educational Websites:
- Domestically Speaking discusses the process of creating a drought-tolerant planter, emphasizing the need for good drainage and the use of suitable materials like lava rock and cactus potting soil.
Glossary of Terms
Sedum: Often referred to as stonecrop, Sedum is a genus of succulent plants known for its hardiness and drought resistance. These are favored in gardens for their easy care.
Echeveria: A large genus of succulent plants that form rosettes and come in a variety of stunning colors and shapes. Echeveria is particularly popular for container gardens.
Kalanchoe: This genus includes succulent plants that boast fleshy leaves and produce brightly colored, bell-shaped flowers. Kalanchoe species are valued for their low-maintenance nature.
Succulent Plants: Plants with thick, fleshy parts adapted to store water. They are ideal for dry climates and soil conditions due to their drought-resistant capabilities.
Drought-Resistant Plants: Plants that have adapted to survive with minimal water. Such adaptations make them suitable for arid conditions.
Dudleya: A genus of succulent plants, Dudleya is native to the southwest U.S. and has a rosette shape. They are adapted to thrive in dry, rocky soils.
Cholla: Also known as Cylindropuntia, cholla is a genus of cacti that is characterized by its segmented branches and spines.
Carpobrotus edulis: Commonly known as the California coastal ice plant, it’s an invasive species in some areas but valued in gardens for its hardy nature and vibrant daisy-like flowers.
Thyme: A drought-resistant herb that can thrive in poor soil, making it a suitable companion in a succulent garden for both its utility and low water needs.
Cup Flower: Small, cup-shaped flowers that often adorn drought-tolerant plants, adding visual interest to low-water gardens.
Aeonium arboreum: A succulent with tall stems and large rosettes. Known for its sculptural qualities and sometimes referred to as tree houseleek.
Echeveria agavoides: A species of Echeveria resembling the agave plant; it’s admired for pointed leaves and a compact rosette form.
Senecio mandraliscae: Commonly called blue chalk sticks, this succulent is appreciated for its long blue-green leaves and ground-covering ability.
Haworthia fasciata: A small, rosette-forming succulent known for its zebra-striped leaves and shade tolerance, unique amongst many sun-loving succulents.
Frequently Asked Questions
Creating a drought-resistant potted garden with succulents involves understanding their arrangements, potting methods, plant selection, and care techniques to ensure they not only survive but thrive.
How can you arrange succulents for an aesthetically pleasing and drought-resistant potted garden?
Arranging succulents for visual appeal and water efficiency involves selecting a variety of shapes and colors. You should also provide ample space between the plants to prevent overcrowding. Lastly, make sure each plant receives adequate sunlight. Incorporating a double dish gardening method can enhance drainage and create an attractive layered look.
What are the steps to creating a succulent container garden that thrives in dry conditions?
To create a succulent container garden optimized for dry conditions, start with a well-draining potting mix. Then, choose containers with drainage holes and position the garden in a location that receives plenty of sunlight. Lastly, regularly monitor the soil moisture to avoid overwatering.
Which succulents are known for their exceptional drought tolerance and are ideal for potting?
Plants like sedeveria and various types of sedum are known for their exceptional drought tolerance and adapt well to potting. These succulents store water in their leaves, making them well-suited for dry environments.
What are best practices for planting cacti in pots to ensure their growth and drought resistance?
When planting cacti in pots, using a well-draining soil mix and pots with adequate drainage is essential. You should also provide sufficient light and water sparingly, allowing the soil to dry out completely between waterings.
How does placing rocks in succulent planters affect the health and drought resistance of the plants?
Adding rocks to the bottom of succulent planters or on top of the soil can improve drainage and help prevent root rot. This, in turn, enhances the drought resistance and overall health of the succulents.
Can succulents be successfully grown in outdoor pots, and if so, what special considerations need to be taken?
Succulents can thrive in outdoor pots if they’re placed in a sunny spot and if the right potting mix is used.
It’s important to understand the specific soil requirements. You should amend the soil as needed to ensure good drainage and aeration.


